How To Deal With an Ingrown Hair on a C-Section Scar
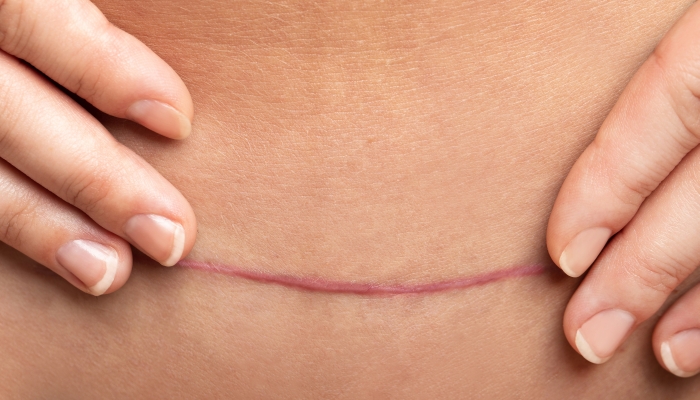
- Ingrown hairs on a C-section scar can be painful and irritating.
- Ingrown hairs can be caused by shaving, tight clothing, and dead skin cells.
- C-section scars normally heal within 6 weeks.
- Ingrown hairs on C-section scars can be treated with mild soap and a warm compress.
Recovering after a C-section requires a lot of care and patience. Postpartum women who have a C-section incision often experience extra discomfort and have to spend extra time avoiding heavy lifting while they wait for their surgical site to heal.
Unfortunately, there are many hair follicles in the same area where the doctor will perform a C-section surgery.
Healing from pregnancy can be difficult enough, but dealing with ingrown hair on a C-section scar can make things even more complicated. Knowing how to take care of ingrown hairs and allow the scar tissue to heal can help you feel more comfortable as you recover from pregnancy and the birth of your baby.
Safe Management of Ingrown Hairs on C-Section Scars
Most ingrown hairs do not need to be treated by a doctor or specialist. As long as you keep the area clean and free of infection, the uncomfortable bump should heal without too much fuss.

Home Remedies and Care
When you’re at home with a new baby and a C-section scar, the last thing you want to worry about is dealing with ingrown hair. Fortunately, there are some easy home remedies you can try to remove dead skin cells and reduce the risk of infection in the affected area.
Warm compresses can be used to soothe the area and encourage healing. Simply apply a warm, moist compress over the painful area for about five minutes. You can use a warm compress twice each day for about a week until you notice improvement.
You can also use gentle exfoliation techniques to remove dead skin cells and soften the skin around your scar line. Using a fine exfoliating soap or washcloth over the bumps on the surface of your skin may help prevent bacteria from getting stuck under the skin.
What to Avoid
While it is very tempting, do your best to avoid picking, squeezing, or shaving over the scar. These actions can cause further irritation and may even lead to infection around your scar.
If the bumps on your skin start to look like a pimple or form a white spot on the surface of your skin, the ingrown hair may be ready to break through. You may hope that popping a bump will alleviate the pressure you feel, but popping may introduce bacteria underneath your skin and can cause an infection.
In addition to avoiding picking at your skin, try to take a break from shaving for a while. Letting your hair grow for a week or two can be enough to eliminate your problem with ingrown hairs.
Understanding C-Section Scars
A C-section is a major surgery, performed by a doctor in a sterile environment in the operating room. Mothers who deliver their babies via C-section should follow their doctor’s advice about how to care for their scars and reduce the risk of complications.
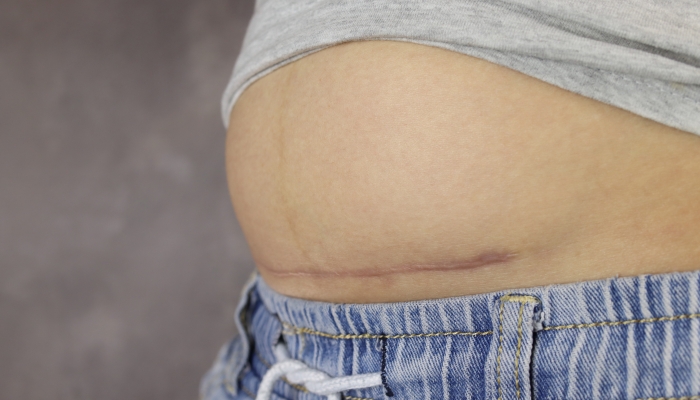
Characteristics of C-Section Scars
When a doctor performs a C-section11. Cesarean Section. Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/cesarean-section, they can perform a vertical (classical) incision or a horizontal (transverse) cut. Both of these types of surgical incisions can lead to scarring. Because a transverse cut is closer to the bikini line, these types of scars are more likely to develop ingrown hairs.
Scars form after a deep cut like a C-section incision because tough scar tissue is laid down by the body in order to bring the skin back together and heal. Your body will go through several stages of healing before your incision is completely healed. Most C-section scars heal within a few weeks, but occasionally, problems arise.
C-section complications include:
- Infection
- Ingrown hairs
- Dehiscence
- Hypertrophic Scarring
To avoid these complications, follow your doctor’s recommendations for rest, keep the area clean and dry, wear loose-fitting clothing, and only apply cream or ointment that has been approved by your physician.
What Causes Ingrown Hairs on C-Section Scars?
Most ingrown hairs22. Ingrown hair: What it looks like, causes, treatment & prevention. . Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17722-ingrown-hair, no matter where they appear on your body, are caused by the same things. Ingrown hairs on C-section scars can be caused by:
- Shaving
- Waxing
- Tweezing
- Wounds over hair follicles
- Tight fitting clothing
Identifying an Ingrown Hair on a C-Section Scar
If you have had ingrown hair before, you probably know what it looks and feels like. Ingrown hairs in the underarm area, on the legs, and in the groin are usually easy to identify. However, you may have a more difficult time differentiating between a healing scar and an ingrown hair.
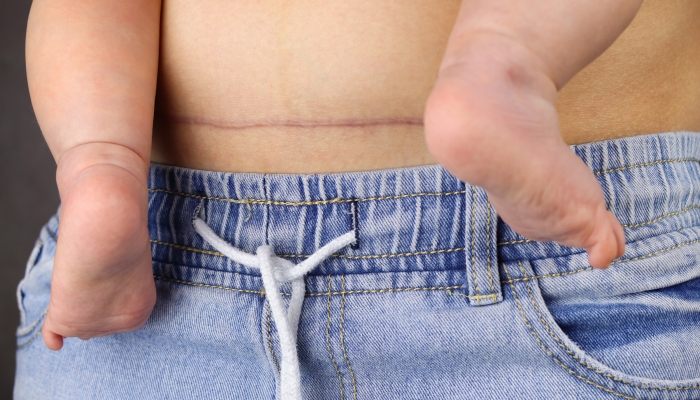
Signs of an ingrown hair include:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Pain
- Pus formation
Signs of a scar healing include:
- Itching
- Redness
- Pink skin
In addition to looking at the differences between scarring and ingrown hairs, pay attention to the timing of the skin irritation. If new bumps appear near your C-section scar within a day or two after shaving, tweezing, or waxing, chances are high that you have developed an ingrown hair.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While most ingrown hairs resolve without medical treatment, infected ingrown hairs near your C-section scar should be discussed with your doctor.
If your ingrown hair is extremely painful, has green or dark yellow stuff leaking out of it, feels hot to the touch, or if you develop a fever, call your doctor for advice.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
If your ingrown hair does become infected, you may need medical treatment to avoid complications.

When Is Medical Intervention Necessary?
Women who develop frequent ingrown hairs around their incision site, have severe pain or swelling associated with their ingrown hairs, or have fevers or other signs of severe illness should seek medical care.
Possible Medical Treatments
Treatment for ingrown hair can range from over-the-counter cream to surgical removal of the hair. Creams may include bacitracin or topical steroids to reduce swelling. Surgery is usually performed using a local anesthetic in the doctor’s office.
Preventive Measures and Long-Term Care
If you can, it’s best to avoid ingrown hairs over your C-section scar, rather than having to treat them later. There are a few simple steps you can take to avoid developing these pesky problems. These include:
- Using an electric razor if you must shave.
- Avoiding tweezing, waxing, or plucking your hairs.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing.
- Keeping the area around your incision clean and dry.
- Wearing special non-irritating C-section underwear.
FAQs
How long after a C-section should I wait before treating ingrown hairs near the scar area?
If you develop ingrown hairs in the area near your C-section scar, you can treat them right away using a warm compress or gentle exfoliation. Do not shave, pick at, pinch, or scratch your ingrown hair, since this can increase the risk of infection.
How can I differentiate between ingrown hair and other complications like keloids or hypertrophic scars on a C-section site?
Ingrown hairs are typically red, raised, bumps that are painful and appear a day or two after shaving, plucking, or waxing the area. Hypertrophic scars do not usually cause pain or irritation, and happen across the entire length of the incision. Ingrown hairs may become infected or ooze pus, while hypertrophic scars do not.
How often should I examine my C-section scar for signs of ingrown hairs or other complications?
It’s a good idea to examine your C-section scar at least once a day for signs of ingrown hairs, wound dehiscence, or infection.
What kinds of medications are typically used to treat infected ingrown hairs?
Topical ointments like bacitracin or hydrocortisone cream may help speed the healing and decrease pain associated with ingrown hairs. If your ingrown hair becomes infected, your doctor may prescribe an oral antibiotic. Common antibiotic medications include azithromycin, clindamycin, penicillins, or cephalosporins.
References
- Cesarean Section. Johns Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/cesarean-section
- Ingrown hair: What it looks like, causes, treatment & prevention. Cleveland Clinic. (2022, March 4). https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17722-ingrown-hair

The information WonderBaby provides is not intended to be, and does not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. Always consult with a qualified medical professional about your specific circumstances.
Related Posts

Pregnancy
What’s a Dye Stealer Pregnancy Test?
A dye stealer pregnancy test usually means that your hCG levels are very high, which is typically considered a good sign for pregnancy.

Pregnancy
Can Yelling Cause a Miscarriage?
Yelling alone can not cause a miscarriage. However, maternal stress can cause high blood pressure, preterm labor, and other health problems.

Pregnancy
I Feel Rejected by My Husband While Pregnant. What Should I Do?
I’m feeling rejected by my husband during pregnancy; how can I help him to open up and improve our relationship? Communication is key to a healthy relationship.